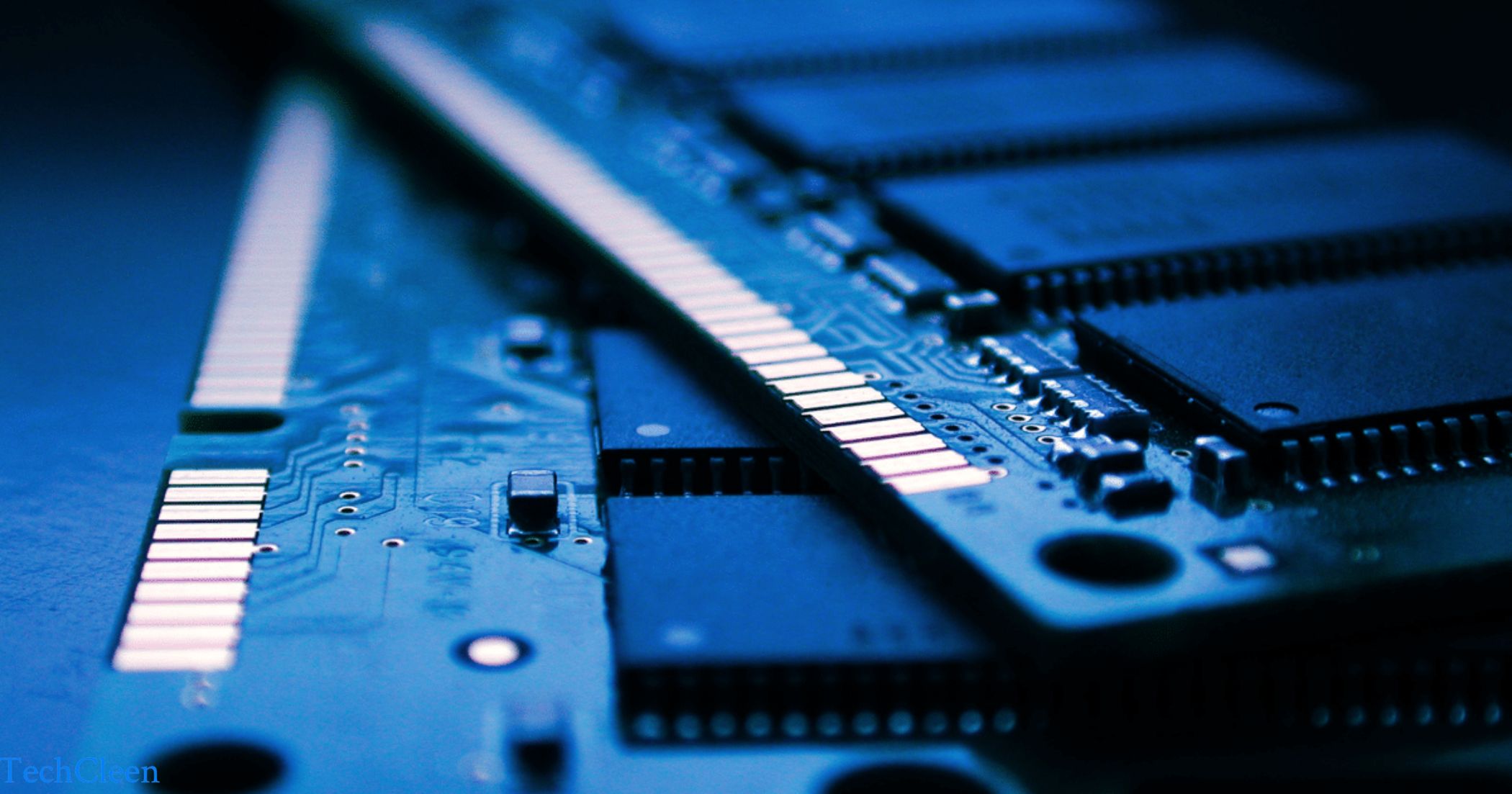
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data access for the processor. It temporarily stores actively used programs and data for quick retrieval. Unlike permanent storage, RAM loses its content when the power is turned off. The amount of RAM affects a computer’s multitasking and overall performance.
RAM is like your computer’s speedy worktable. It helps your computer think fast and do many things at once. Imagine it as a quick, forgetful helper – it holds info only when your computer is on, so when it’s off, everything goes bye-bye. Having more RAM is like giving your computer a bigger worktable for juggling tasks and being super quick.
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a fast, volatile computer memory that stores active data for quick access by the processor. Unlike permanent storage, RAM loses its contents when the computer is turned off. The quantity of RAM affects a computer’s multitasking ability and overall speed. It acts as a temporary workspace for the processor to efficiently handle ongoing tasks.
Types of Ram

There are various types of RAM (Random Access Memory). The main types include:
1.DRAM (Dynamic RAM): Requires constant refreshing to maintain data, commonly used in system memory.
2. SRAM (Static RAM):Doesn’t need refreshing, faster but more expensive than DRAM, often used in cache memory.
3. DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous DRAM): An improved version of SDRAM, widely used in modern computers with variations like DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4.
4. VRAM (Video RAM): Specialized for graphics processing in GPUs, ensuring smooth video performance.
5. LPDDR (Low Power DDR): Designed for mobile devices, offering power efficiency.
These types differ in their speed, power consumption, and specific use cases.
Understanding the Functionality of RAM

RAM, or Random Access Memory, works as a temporary and fast storage system for data that the computer’s processor actively uses during its operation. Here’s a simplified explanation of how RAM works:
1. Storage of Data: When you open a program or file, the relevant data is loaded from the slower and more permanent storage (like hard drives or SSDs) into the RAM.
2. Quick Access: The processor can quickly access any piece of data in RAM, regardless of its location. This is in contrast to the sequential access used in traditional storage devices.
3. Temporary Nature: RAM is volatile memory, meaning it loses its content when the power is turned off. This characteristic allows it to be quickly read and written to, making it ideal for temporary storage.
4. Faster than Storage: RAM is much faster than traditional storage devices, which enables the computer to perform tasks more quickly. The speed of RAM is crucial for the overall speed and responsiveness of a computer.
5. Multitasking: RAM allows the computer to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. Each open application and its associated data are stored in RAM, allowing the processor to quickly switch between tasks.
In summary, RAM provides the necessary speed and quick accessibility that the processor needs to efficiently execute tasks, making it a critical component for a computer’s performance, especially during multitasking.
The Importance of RAM for Your Computer

RAM, or Random Access Memory, is an indispensable component for the optimal functioning of a personal computer. Its essential role lies in providing swift access to actively used data and programs for the computer’s processor. When you open applications or run tasks, the relevant data is loaded from the slower and more permanent storage (like hard drives or SSDs) into the RAM.
This enables the processor to quickly retrieve and manipulate the data, significantly boosting the overall speed and responsiveness of your PC. Moreover, RAM facilitates efficient multitasking. The more RAM your system has, the better it can juggle multiple tasks simultaneously without slowing down. Each open application, browser tab, or document occupies a portion of the RAM, allowing the processor to seamlessly switch between them.
In essence, RAM acts as a dynamic workspace for the processor, enhancing your computer’s ability to handle diverse and demanding computing tasks. Thus, a sufficient amount of RAM is crucial for a smooth and efficient computing experience, ensuring that your PC can handle the demands of modern software and applications.
Under What Circumstances Can a PC Operate Without RAM?
In general, a personal computer cannot function without RAM due to its fundamental role in providing quick and temporary storage for actively used data. However, there are some specialized scenarios where a computer-like device may operate with minimal or no traditional RAM. Embedded systems, such as certain types of microcontrollers or dedicated hardware, might utilize other forms of non-volatile memory or onboard memory that serve similar purposes on a smaller scale.
These exceptions, though, are specific to certain applications and are not representative of the standard architecture of general-purpose computers. For typical desktops, laptops, and servers, RAM remains an essential component for the basic operation of the system and the execution of various tasks.
Identifying Signs of RAM Failure
Recognizing signs of RAM failure is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance of a computer system. One common indicator is frequent system crashes or spontaneous reboots, often accompanied by error messages indicating memory-related issues. Sluggish performance, despite a system not running resource-intensive applications, can also be a red flag. If applications take longer to load, freeze, or unexpectedly close, it may indicate potential problems with the RAM.
Another symptom is the appearance of the infamous “blue screen of death” on Windows systems, which can be triggered by faulty RAM. To identify such issues, users can run diagnostic tools or memory tests, checking for errors that may point to RAM problems. Regular monitoring and timely identification of these signs allow users to address and replace malfunctioning RAM modules, ensuring the continued reliability of their computer systems.
Frequently asked question
What happens if you run a computer without RAM?
If you run a PC without RAM, you cannot pass through the POST. If you turn on a PC without RAM, you may hear several beeps or see several LED flashes, showing that the RAM is missing. Then, the PC won’t boot up. This article explains what high memory usage is and how to check it.
Is RAM necessary for a computer to run?
Random access memory, more commonly called RAM, is the key to your computer working properly. This is especially true with today’s memory-hungry applications – such as office programs, multimedia editing packages, and graphics-intensive games.
Which RAM is faster?
DDR4 speeds start at 2400 MT/s and offer faster speeds and responsiveness than all other generations of memory. Optimized for gamers, professional designers, and enthusiasts who need to maximize data rates, DDR4 is for those who want the most from their system.
Can a PC run without SSD?
Should be fine. Depending on where the slots are on that board putting the SSD in after it’s assembled may be annoying though, you can just install the CPU, cooler, and RAM while the motherboard sits on top of its box, then plug in the GPU for a POST (Power On Self-Test, just booting to BIOS).
Is RAM faster than SSD?
SSDs use a special type of memory circuitry called non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) to store data, so everything stays in place even when the computer is turned off. Even though SSDs use memory chips instead of a mechanical platter that has to be read sequentially, they’re still slower than RAM.
final conclusion
In conclusion, a computer cannot function properly without RAM (Random Access Memory). RAM plays a pivotal role in providing quick and temporary storage for actively used data, allowing the processor to swiftly access and manipulate information. Its volatile nature makes it essential for dynamic tasks and multitasking, as it loses its content when the power is turned off.
While there may be exceptions in specialized devices or embedded systems that operate with minimal or alternative forms of memory, for standard desktops, laptops, and servers, having RAM is fundamental for the basic operation and efficient performance of the computer. It remains an integral component in ensuring the smooth execution of tasks and responsiveness of the system.

With a robust five-year background in the ever-evolving realm of tech gadgets, I bring a wealth of hands-on experience and a deep understanding of the latest technological advancements.