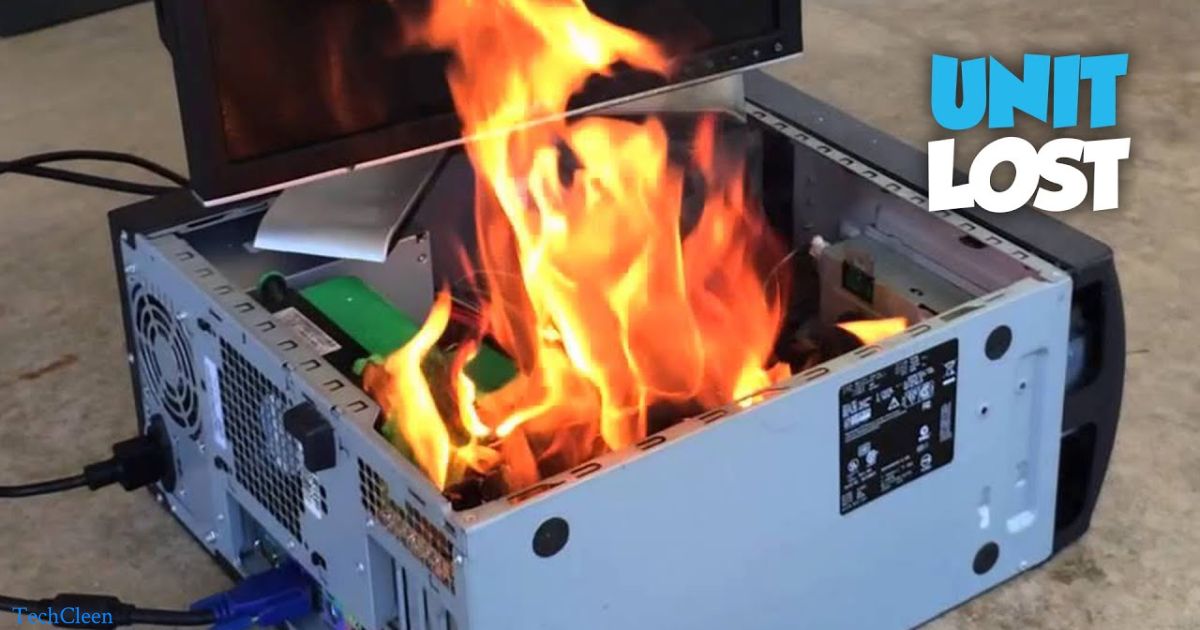
The concern of computer explosions arises from overheating, notably in laptops with lithium-ion batteries. While the typical explosion scenario is unlikely, overheating poses a potential risk. Desktops generally limit damage to the power supply, but laptops, especially with lithium-ion batteries, may face an increased risk of internal damage and potential explosion under extreme heat.
Contemplating the unlikely yet intriguing scenario of computers exploding invites us to explore the boundaries of electronic safety. Beyond the typical hardware concerns, the concept gains traction, particularly with overheating laptops equipped with lithium-ion batteries.
Computers are not designed to explode; they have safety features to prevent such events. While overheating can occur and potentially cause damage, explosions are highly unlikely. Adhering to safety guidelines and maintaining proper usage can minimize risks.
Ageing of the CPU

As a computer ages, the potential for overheating becomes a significant concern, particularly with outdated hardware unable to keep up with the demands of newer, resource-intensive applications and games. The discrepancy between aging components and the increasing complexity of modern software places stress on the system, leading to heightened temperatures.
For instance, a CPU from 2014 may struggle to cope with the demands of 2020’s resource-heavy applications, causing it to generate more heat and increasing the risk of damage. Recognizing the limitations of an aging PC and considering upgrades or modifications becomes crucial to maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential overheating issues. In essence, relying on an older CPU to run contemporary titles poses a real threat to the system’s stability.
The disparity between the evolving demands of modern software and the capabilities of an outdated CPU results in increased stress on the hardware, manifesting as overheating. This underscores the importance of acknowledging the limitations of aging hardware, prompting users to consider upgrading components or investing in newer systems to ensure a smoother and more sustainable computing experience.
Lithium-Ion Battery
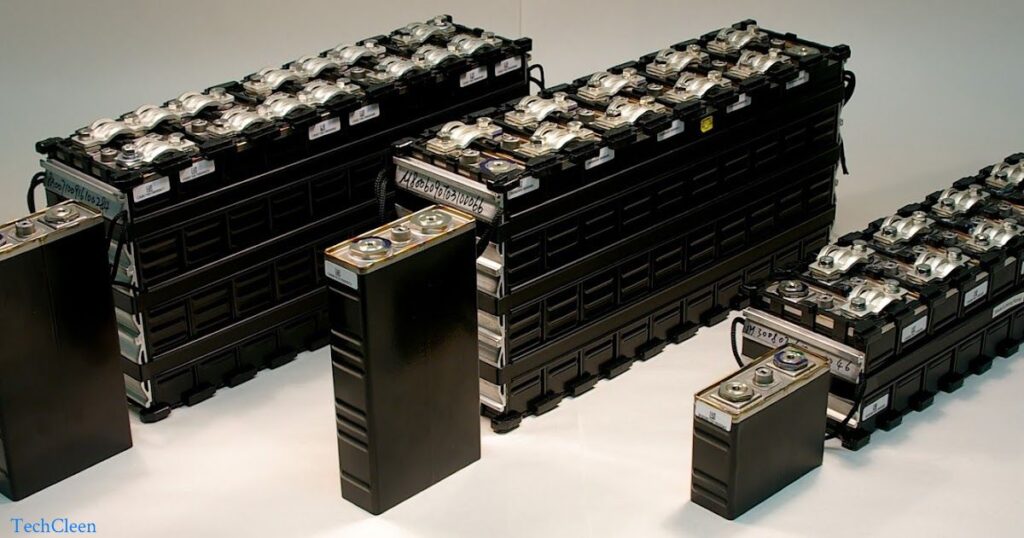

Lithium-ion batteries have become a staple in contemporary gadgets, finding widespread use in mobile phones and laptops. Despite their convenience, these batteries are susceptible to wear and tear, with a rare but acknowledged risk of damage leading to potential explosions. While such incidents are infrequent, it underscores the importance of proactive measures.
For users with laptops featuring lithium-ion batteries, a prudent approach involves replacing the battery every two to three years. This regular maintenance helps mitigate the risk of damage, ensuring the continued safe and reliable operation of devices powered by these batteries. The widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries in modern electronics highlights their efficiency and capacity, yet their vulnerability to wear and potential damage remains a concern. To maintain the longevity and safety of devices, particularly laptops and mobile phones, users are advised to stay vigilant.
The recommended replacement of lithium-ion batteries every two to three years serves as a preventive measure, providing a reliable strategy to manage the inherent risks associated with these widely used energy storage components.
Overheating Concerns
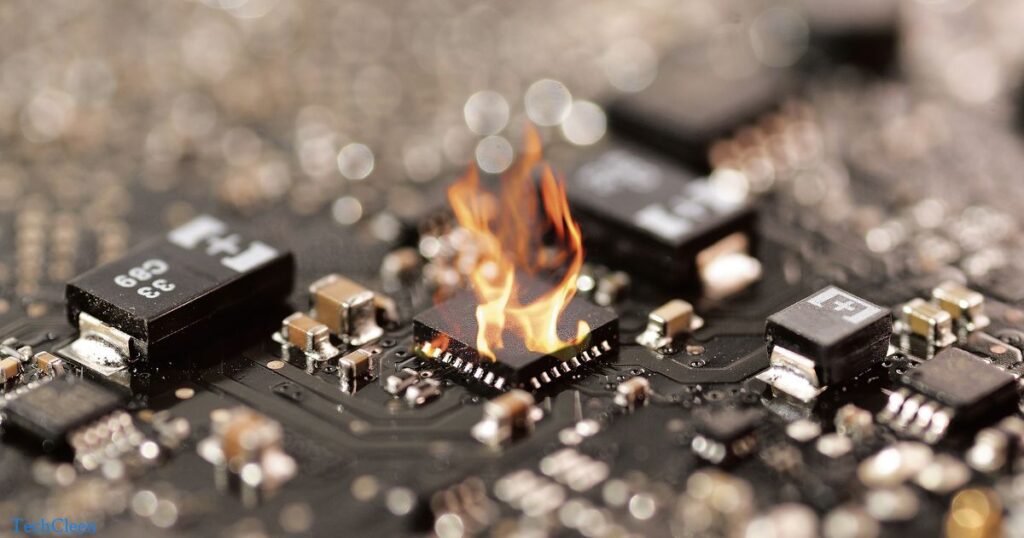
Excessive heat poses a significant threat to the overall health of a PC, particularly when pushing it to its limits through intense graphic gaming or overclocking. When temperatures surpass 85 degrees Celsius, the risk of damage to neighboring components increases substantially. To mitigate this risk, opting for effective cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling or other cooling options, becomes crucial to maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing potential harm to the PC.
Despite the concerns associated with excessive heat, the notion that a PC will explode after running continuously for 24 hours is unfounded. While prolonged use, especially during demanding tasks like gaming, can elevate temperatures and stress components, modern PCs are designed with safety measures. Running a PC overnight or under heavy load may lead to increased wear and tear, but the likelihood of explosions or severe damage is minimal. It emphasizes the resilience of well-maintained systems and the importance of implementing proper cooling strategies to ensure the longevity and stability of the PC.
Risk of Explosion: Swollen Laptop Batteries
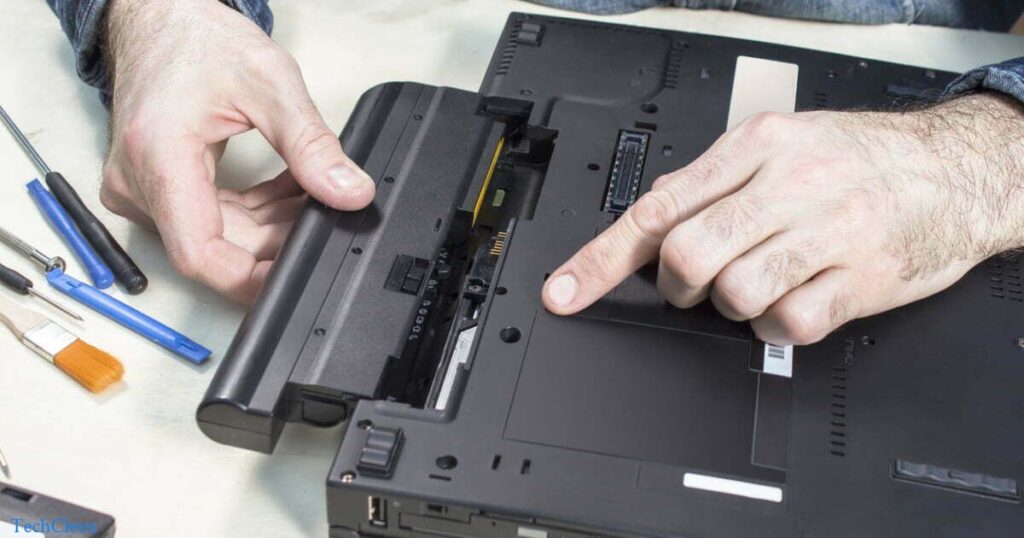

A swollen laptop battery poses a risk of exploding. Swelling in a lithium-ion battery typically occurs due to internal chemical reactions or manufacturing defects. The swelling is a sign of gas buildup within the battery, which can lead to increased pressure. In extreme cases, the pressure buildup may result in the battery rupturing or exploding. It’s essential to address a swollen battery promptly by discontinuing use, removing it from the laptop, and seeking professional assistance or replacement to mitigate the potential risks associated with an exploding battery.
Potential Laptop Explosion Due to Overheating
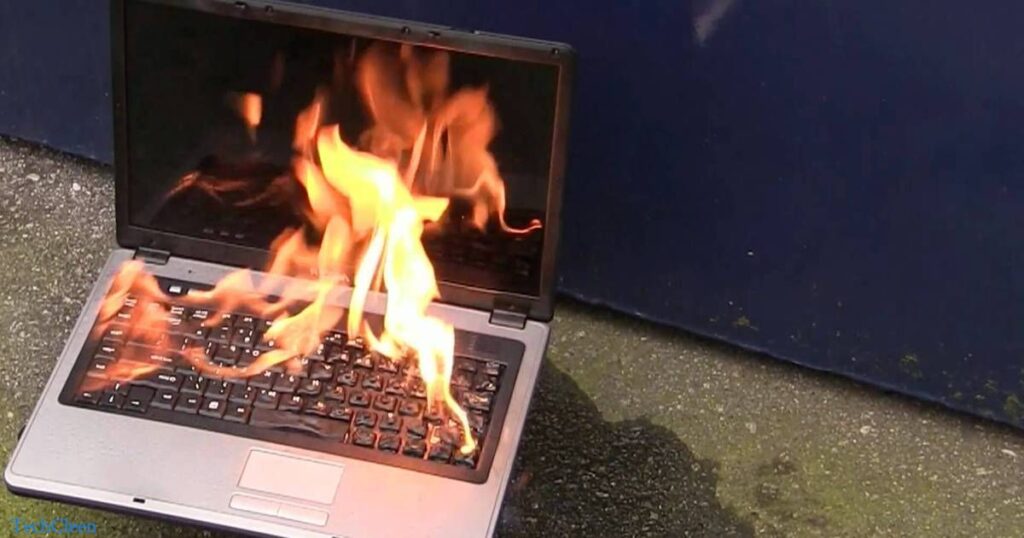

While it’s extremely rare, a laptop can potentially explode from overheating under certain extreme circumstances. Overheating may lead to critical failures in internal components, especially the lithium-ion battery. If the temperature becomes excessive, it can cause thermal runaway in the battery, leading to gas buildup and potential rupture or explosion.
However, modern laptops are designed with safety features to minimize these risks. It’s crucial to practice proper cooling measures, avoid blocking ventilation, and monitor system temperature to reduce the likelihood of overheating-related issues.
Is there a Risk of a Laptop CPU Explosion?
The likelihood of a CPU in a laptop exploding is extremely rare under normal operating conditions. CPUs (Central Processing Units) are designed with multiple safety features, including thermal protection mechanisms that throttle performance or shut down the system to prevent damage from overheating.
However, in highly unusual situations, such as extreme overclocking without adequate cooling or manufacturing defects, a CPU could theoretically be damaged to the point of failure. Despite these rare possibilities, the typical use of a laptop, even under heavy workloads, should not result in a CPU explosion.
Preventing PC Explosions: Safety Measures
Optimal Ventilation and Dust Management:
Keeping your PC dust-free is vital for optimal functioning. Utilize a blower to clear dust clogs and ensure proper ventilation around the CPU. This proactive approach helps prevent overheating and maintains the overall health of your system.
Electrical Safety with Levegra Surge Protector:
Protect your PC against electrical issues and surges by incorporating a reliable surge protector like Levegra. This essential device acts as a barrier, safeguarding your PC components from potential damage caused by electrical fluctuations. It serves as a valuable investment in ensuring the long-term safety and stability of your computer.
Responsible Overclocking Practices:
Avoid overclocking the CPU beyond recommended limits to prevent overheating. Overclocking can lead to increased stress on the system, potentially compromising its safety. Adhering to recommended settings ensures a balance between performance and temperature.
Proactive Temperature Monitoring:
Regularly monitor your CPU temperature using software tools. This proactive measure allows you to detect and address temperature spikes promptly, reducing the risk of overheating and potential damage to your PC components.
Professional Maintenance and Troubleshooting:
Consider seeking assistance from professionals for comprehensive CPU maintenance and troubleshooting. Experts can provide specialized care, addressing potential issues and ensuring the longevity of your PC. Their expertise adds an extra layer of assurance to the safety and reliability of your computer system.
Frequently asked question
What can cause a computer to explode?
Thermal runaway can lead to an explosion when there is a problem that’s causing the battery to produce more heat than it can handle. Lithium-ion batteries can be damaged by excessive storage heat of over 60 degrees Celsius, overcharging, manufacturing defects, and product tampering.
Can a laptop burst?
Yes, a laptop can potentially explode from overheating, although this is a relatively rare occurrence.
Can a game melt your PC?
We’re here to clarify the situation, so don’t be afraid. In actuality, your laptop or computer won’t necessarily die if you play games on it. These contemporary devices have powerful CPUs, high-performance graphics cards, and plenty of memory because they are designed to withstand the rigors of gaming.
Can an unplugged laptop catch fire?
Technically, yes. But in very limited (and highly unlikely) circumstances. The first would be some kind of out-of-control meltdown in the CMOS battery (or the laptop battery if a laptop). Not common, but not unheard of.
Can a computer explode from a virus?
It’s very dependent on the type of virus and the type of hardware in question. It is possible, with some stipulations, but it’s almost always amazingly unlikely. Computers are not organic and biologic lifeforms like we are.
Final conclusion
In navigating the complexities of PC safety and the risk of explosions, a proactive approach is paramount. Implementing a combination of learned tips and industry best practices, such as keeping the PC dust-free, ensuring optimal ventilation, forms a robust foundation for safeguarding against potential electrical issues and overheating.
Responsible overclocking practices and regular temperature monitoring contribute further to maintaining a balanced system. While the risk of a computer exploding is extremely rare under normal conditions, adhering to these safety measures significantly minimizes potential hazards.
In essence, the fusion of learned experiences and foundational safety practices creates a resilient defense against the unlikely event of a PC explosion. Regular maintenance, professional assistance when needed, and staying informed about evolving technologies collectively contribute to a safe and reliable computing experience.

With a robust five-year background in the ever-evolving realm of tech gadgets, I bring a wealth of hands-on experience and a deep understanding of the latest technological advancements.