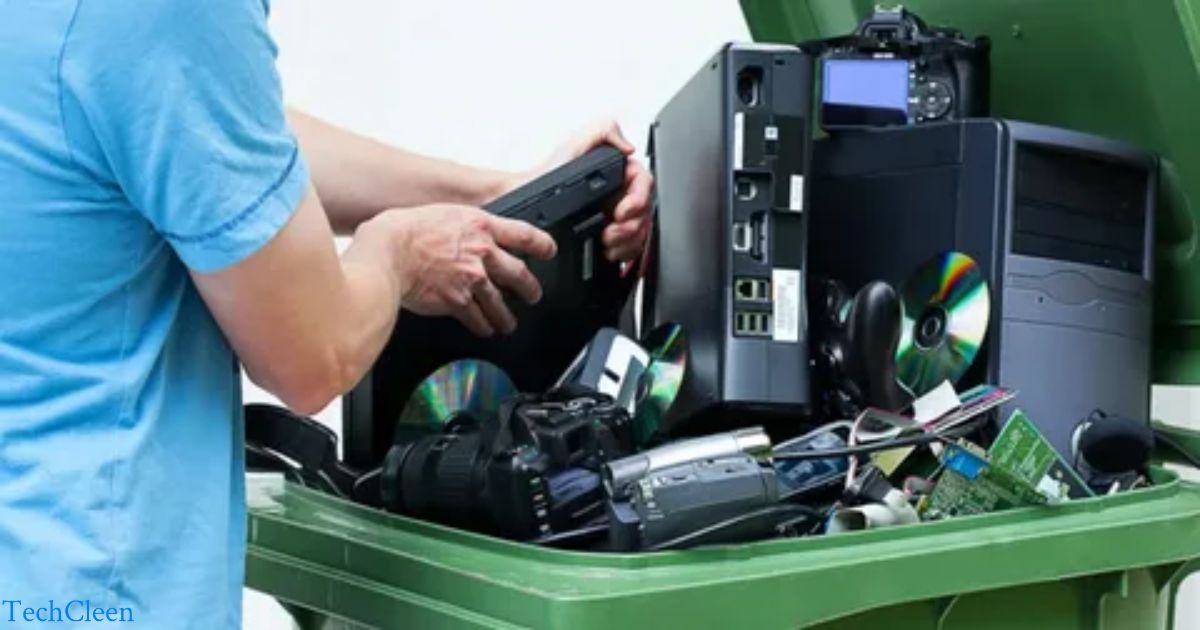
Computer recycling involves dismantling obsolete computers to recover valuable materials like metals and plastics. The process aims to reduce electronic waste, ensuring proper disposal of hazardous components. Through this sustainable practice, valuable resources are conserved, and environmental impact is minimized. It promotes responsible management of electronic waste.
Dismantling the past, computer recycling breathes new life into outdated technology. How Are Computers Recycled? It’s a transformative journey, recovering valuable materials and minimizing electronic waste. In this eco-conscious endeavor, we responsibly manage hazardous components, ensuring a sustainable approach to computing. Join the movement – where recycling becomes the key to a greener future.
Computer recycling is the eco-friendly practice of dismantling outdated computers to recover valuable materials such as metals and plastics. This process minimizes electronic waste, promotes responsible disposal of hazardous components, and contributes to a sustainable approach to computing.
How Computer Recycling Operates?
Computer recycling is a meticulous process that involves the careful disassembly and extraction of valuable materials from outdated or obsolete computers. The first step typically includes the dismantling of electronic devices, separating components like circuit boards, hard drives, and peripherals. Following this, the materials are sorted and processed, with specific attention to extracting valuable resources such as metals and plastics.
Efficient separation technologies, including shredding and magnetic separation, play a crucial role in isolating different materials for recycling. The final stages often include visual inspection, hand sorting, and advanced separation techniques to ensure the highest quality of extracted materials. Once the various components are separated, they can be processed for reuse or sent to specialized facilities for further treatment.
Recycling not only minimizes electronic waste but also contributes to sustainable practices by conserving valuable resources and reducing environmental impact. Overall, the systematic approach to computer recycling helps address the challenges posed by the disposal of electronic waste and promotes a more responsible and eco-friendly management of technology lifecycle.
What Does the Process Entail?
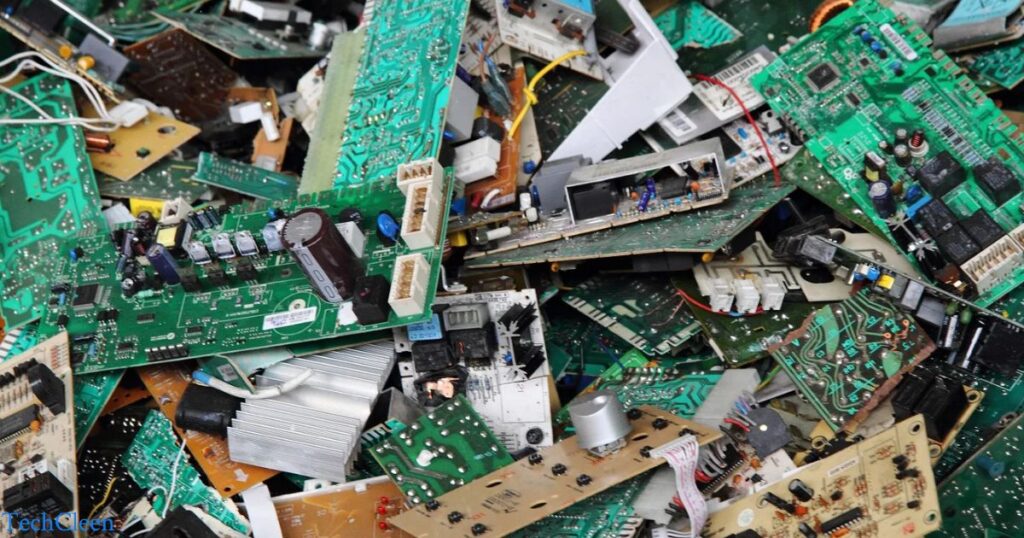

The computer recycling process is a comprehensive series of steps designed to recover valuable materials from outdated or obsolete computers while minimizing environmental impact. It begins with the careful dismantling of electronic devices, including the separation of components like circuit boards, hard drives, and other peripherals.
The subsequent sorting phase categorizes materials for further processing, with a focus on the extraction of valuable resources such as metals and plastics. Efficient separation technologies, such as shredding and magnetic separation, play a pivotal role in isolating different materials to create clean commodity streams. Once separated, materials like ferrous and non-ferrous metals, plastics, and circuit boards undergo additional processing steps, including visual inspection and hand sorting, to improve the quality of the extracted materials.
Advanced separation techniques may also be employed to isolate specific types of plastics, enhancing the potential for reuse. Overall, the computer recycling process aims to promote sustainability by responsibly managing electronic waste, reducing resource depletion, and contributing to a circular economy.
Reasons to Recycle Your Computer
Recycling your old computer is a good idea for a few simple reasons. Computers have stuff in them that can be harmful, so recycling keeps those harmful things from going into landfills. It also means we don’t need as many new materials to make more devices. Parts from old computers, like plastic and glass, can be used again.
When we recycle, it helps groups in the community get computers they need but might not be able to afford. Plus, recycling computers creates jobs, helps people learn new skills, and supports our local economy. Just make sure to pick a good company to recycle your computer. Some companies don’t follow the rules and can cause problems like dumping waste illegally. So, before you recycle, check that the company is trustworthy. A good company will be happy to explain how they recycle computers.
Shredding
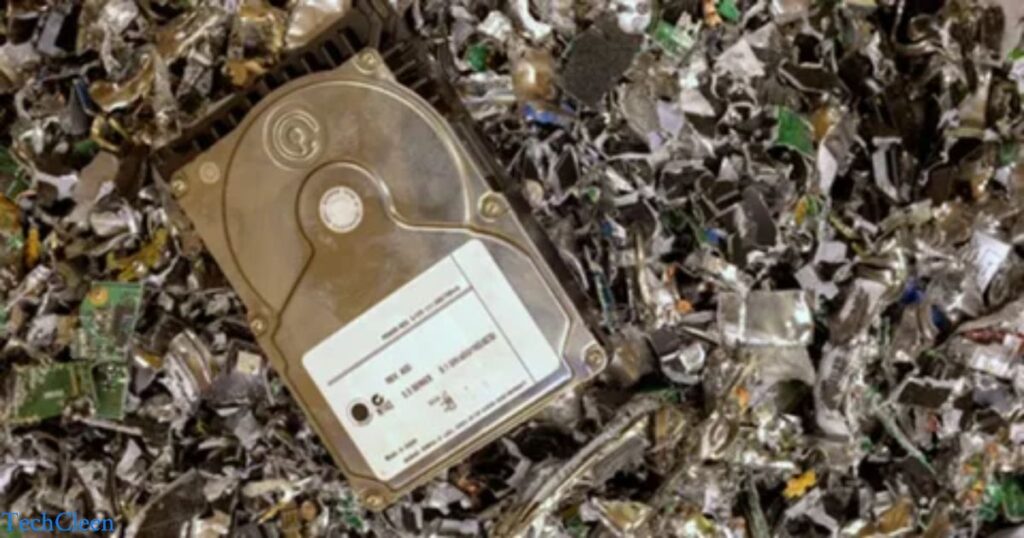

Shredding is a crucial step in the computer recycling process, playing a key role in breaking down electronic devices into smaller components for further separation and processing. During the shredding phase, outdated computers and electronic equipment are mechanically disassembled, reducing them to smaller pieces. This process facilitates the separation of materials like plastics, metals, and circuitry, making it easier to extract valuable resources from the electronic waste.
Once the devices are shredded, powerful magnets are often employed to separate ferrous metals like iron and steel from the mixture, allowing for efficient sorting. Shredding not only aids in the recovery of recyclable materials but also ensures that potentially harmful components are processed in a controlled and systematic manner. This method is integral to the overall goal of computer recycling, contributing to resource conservation, environmental sustainability, and responsible electronic waste management.
Commodity Sorting
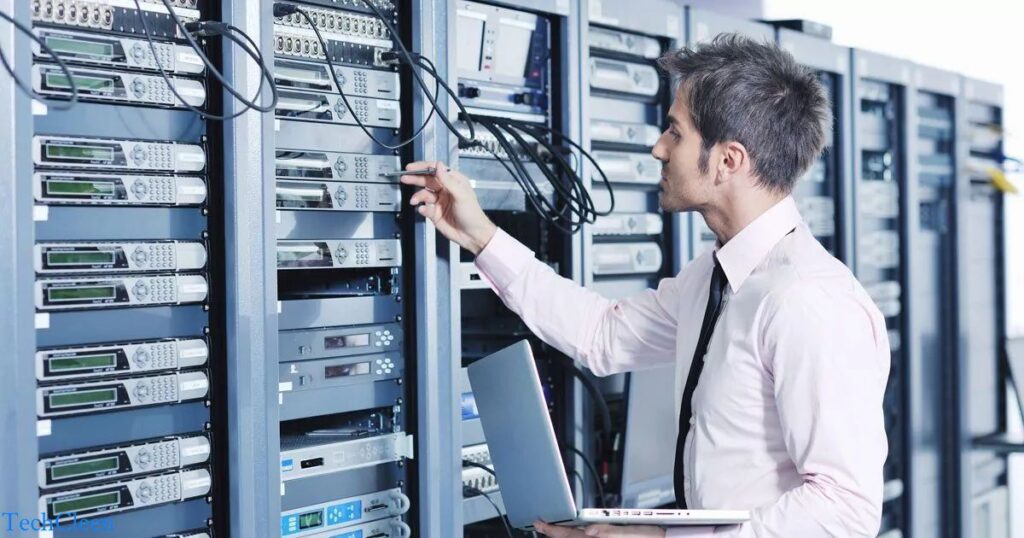

Sorting of commodities is a vital stage in the computer recycling process, where the materials extracted from shredded electronic devices are meticulously organized into distinct categories. This phase involves the separation of various components like plastics, metals, and circuit boards, each destined for specific recycling pathways. Advanced technologies, such as conveyor belts and automated sorting systems, are often employed to enhance the efficiency of this process.
Efficient sorting not only ensures the isolation of valuable materials like copper, aluminum, and high-quality plastics but also plays a crucial role in minimizing waste and environmental impact. The organized streams of commodities obtained through sorting are then prepared for further processing or sale as recycled materials. This step reflects a commitment to sustainable practices, contributing to the circular economy by reducing the need for raw materials and promoting responsible resource management in the realm of electronic waste.
Frequently asked question
What parts of a computer are recycled?
glass, plastic, metal, and circuit board components. For example, your computer’s circuit board contains silver and copper, and the microprocessor is laced with gold. This isn’t just to make your circuit board look pretty.
How much of a computer is actually recycled?
E-waste comprises 70% of our overall toxic waste. Only 12.5% of E-Waste is recycled. 85% of our E-Waste are sent to landfills and incinerators are mostly burned, and release harmful toxins in the air! Electronics contain lead which can damage our central nervous system and kidneys.
How are computer chips recycled?
Microchips, also known as integrated circuits, are typically recycled through a process called “urban mining.” This involves extracting valuable materials, such as gold, silver, and copper, from electronic waste, including old computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices that contain microchips.
Why are computers recycled?
Recycling computers allows reuse of metals, plastic and glass among other items. The availability of this recycled material reduces demand for newly mined virgin material.
Can computers be reused?
If you have a computer that is in good condition, it could be sold or donated for reuse or to charity.
Final conclusion
In conclusion, the computer recycling process is a systematic and essential journey that involves careful disassembly, shredding, and sorting of electronic devices to extract valuable materials. From the initial steps of breaking down outdated computers to the meticulous sorting of commodities like metals and plastics, the recycling process is designed to minimize environmental impact and contribute to sustainable practices.
Advanced technologies and responsible handling ensure the efficient recovery of resources and the reduction of electronic waste. As we navigate the challenges of technological advancement, embracing computer recycling not only promotes a circular economy but also fosters environmental responsibility, job creation, and community support. Choosing reputable recycling companies further ensures that this process is conducted ethically, reinforcing the importance of responsible electronic waste management in our ever-evolving technological landscape.

With a robust five-year background in the ever-evolving realm of tech gadgets, I bring a wealth of hands-on experience and a deep understanding of the latest technological advancements.